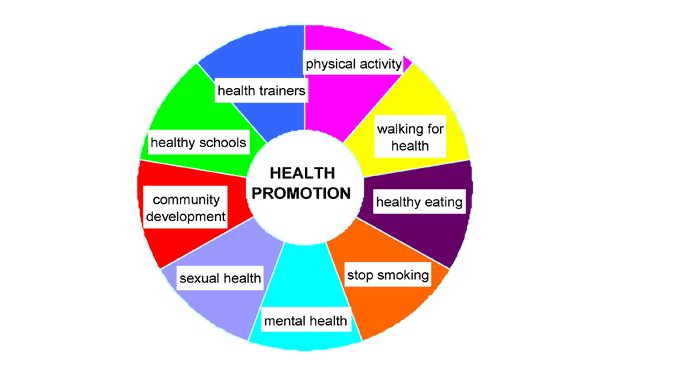
What Is Health Promotion?
We all understand that promoting good health is in everyone’s best interest, but what about health promotion ideas? The fact is that there are hundreds of health promotion concepts, strategies, concepts and “buzzwords” out there and many are based on solid research and evidence. Health promotion theory is important, but the reality is that most of the health promotion strategies promoted by large health organizations and other stakeholders involve a marketing approach that emphasizes advertising rather than listening to what people want and need.
Health Promotion Ideas
Health promotion ideas may include well-being programs such as wellness classes, exercise, weight loss, stress management, healthy food and product choices, support for complementary and alternative health services, and so on. However, studies have shown that the majority of health promotion activities don’t produce the desired results, because the strategies are not well-thought-out, implemented, or monitored. There is a need for health promotion execution that involves not only well-being initiatives but also strategies that address several important health outcomes. Research has shown that health promotion theories must be well-thought-out and comprehensive in order to be effective. Evidence-informed health promotion strategy planning that includes both empirical and conceptual research and engages key stakeholders, patients and community members in the implementation process yields better outcomes.
Health Promotion Researchers And Promotions
According to some health promotion researchers and practitioners, if health promotion efforts focus on prevention rather than on treatment, they will have a limited impact on morbidity and mortality. Prevention efforts that do not include public policy initiatives can only achieve a portion of the goals. In fact, they may even make them worse. Moreover, preventing diseases through education, information and surveillance is a much cheaper and more effective public health practice than trying to treat them once they have developed.
Influencing Behavior
Public health …